Lesson 1. What is Raster Data
Fundamentals of Raster Data in Python - Intermediate earth data science textbook course module
Welcome to the first lesson in the Fundamentals of Raster Data in Python module. The GeoTIFF file format is often used to store raster data. Learn how to to open and explore raster data stored as GeoTIFF files in Python.Chapter Four - Fundamentals of Raster Data in Python
In this chapter, you will learn fundamental concepts related to working with raster data in Python, including understanding the spatial attributes of raster data, how to open raster data and access its metadata, and how to explore the distribution of values in a raster dataset.
Learning Objectives
After completing this chapter, you will be able to:
- Open raster data using Python.
- Be able to list and identify 3 spatial attributes of a raster dataset: extent, crs and resolution.
- Explore and plot the distribution of values within a raster using histograms.
- Access metadata stored in a GeoTIFF raster file via TIF tags in Python.
What You Need
You will need a computer with internet access to complete this lesson.
The data story on Lidar data reviews the basic principles behind Lidar raster datasets.
In previous chapters you learned how to use the open source Python package Geopandas to open vector data stored in shapefile format. In this chapter you will learn how to use the open source Python packages rasterio combined with numpy and earthpy to open, manipulate and plot raster data in Python. In this chapter, you will learn how to open and plot a lidar raster dataset in Python. You will also learn about key attributes of a raster dataset:
- Spatial resolution
- Spatial extent and
- Coordinate reference systems
What is a Raster?
Raster or “gridded” data are stored as a grid of values which are rendered on a map as pixels. Each pixel value represents an area on the Earth’s surface. A raster file is composed of regular grid of cells, all of which are the same size.
You’ve looked at and used rasters before if you’ve looked at photographs or imagery in a tool like Google Earth. However, the raster files that you will work with are different from photographs in that they are spatially referenced. Each pixel represents an area of land on the ground. That area is defined by the spatial resolution of the raster.
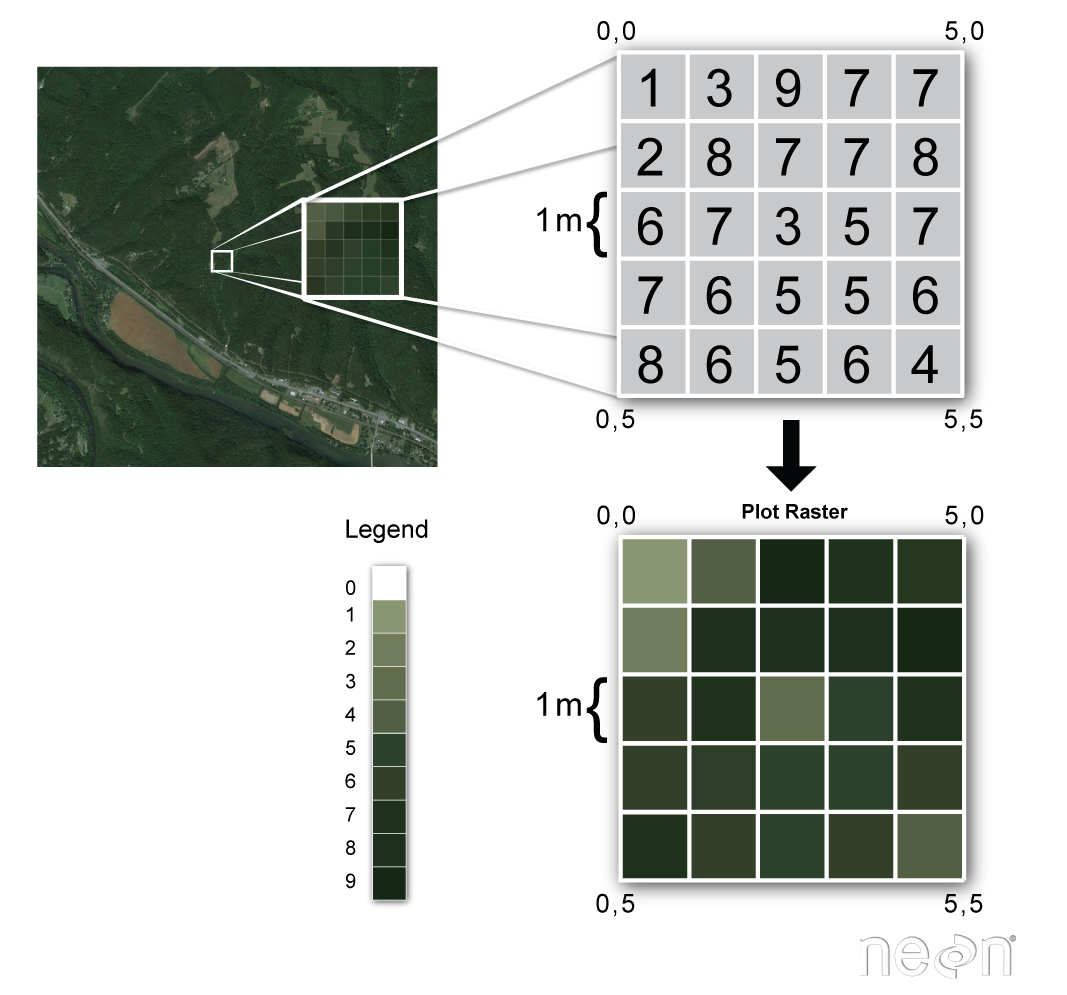
Raster Facts
A few notes about rasters:
- Each cell is called a pixel.
- And each pixel represents an area on the ground.
- The resolution of the raster represents the area that each pixel represents on the ground. So, a 1 meter resolution raster, means that each pixel represents a 1 m by 1 m area on the ground.
A raster dataset can have attributes associated with it as well. For instance in a Lidar derived digital elevation model (DEM), each cell represents an elevation value for that location on the earth. In a LIDAR derived intensity image, each cell represents a Lidar intensity value or the amount of light energy returned to and recorded by the sensor.

In the next lesson, you will learn how to open a lidar raster dataset in Python.
Share on
Twitter Facebook Google+ LinkedIn