Lesson 7. Submit a pull request on the GitHub website Intro version control git
Learning objectives
At the end of this activity, you will be able to:
- Submit a pull request to a repo suggesting changes using github.com
- Define base fork vs. head fork
What you need
- A GitHub user account
- A terminal running bash, and
- Git installed and configured on your computer.
Follow the setup instructions here:
You have now learned how to:
Forka repo in someone else’s github account to your github accountClonethis repo to your local computer- Edit copies of that cloned repo locally on your computer
add,committhose edits to your git repo locallyPushthe committed edits back to your fork
In this lesson, you’ll learn how to submit a pull request to suggest that your edits are included in another (the central Earth Lab) repo.
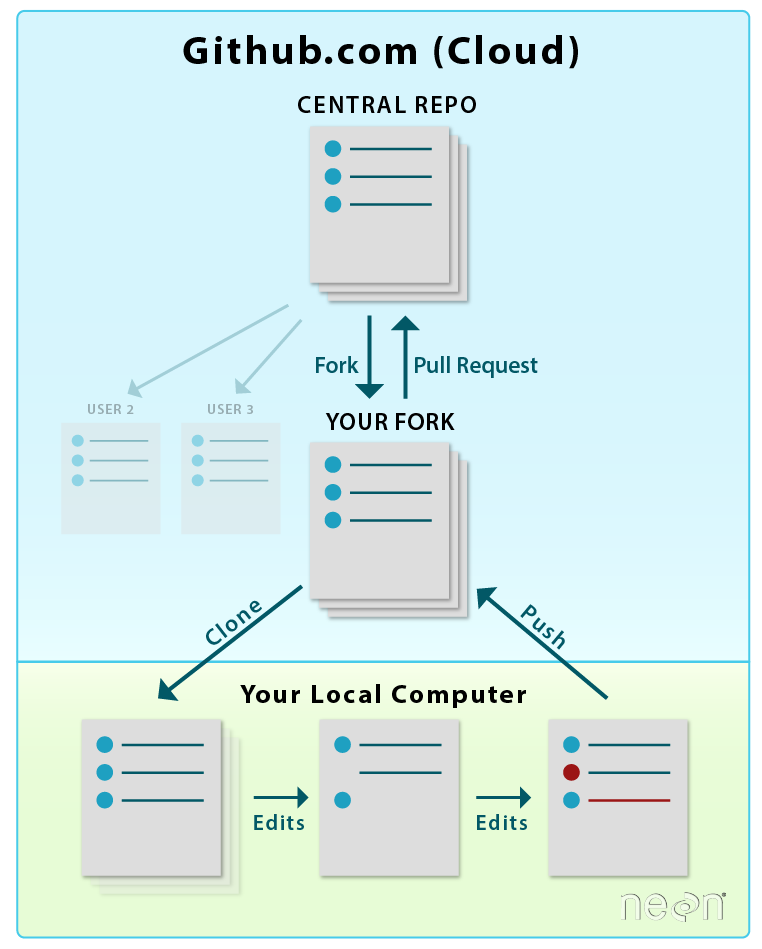
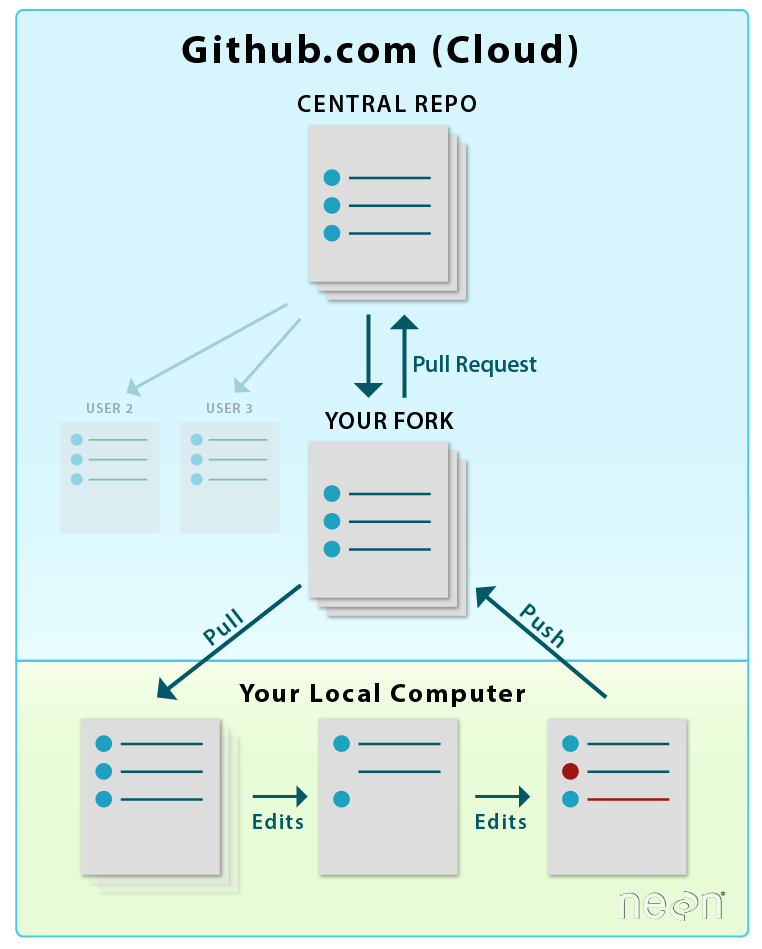
git pull . Notice that the workflow is
similar in both images above, however the commands are different the first time
you setup your repo in your GitHub account and on your local computer!
Source: National Ecological Observatory Network (NEON)
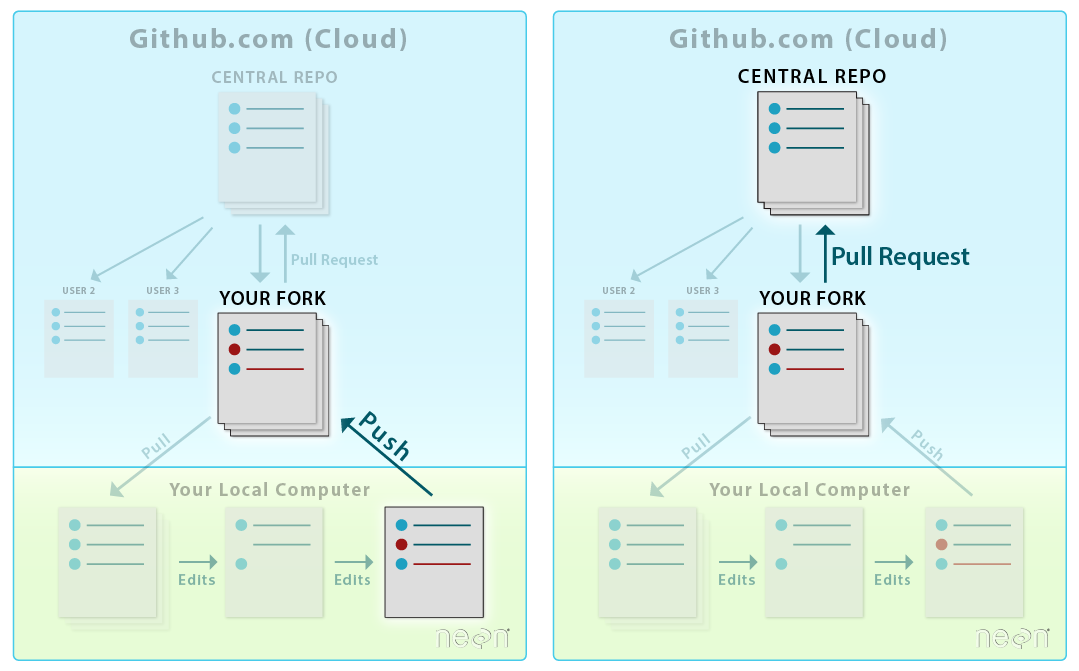
About pull requests
A pull request to another repo is similar to a “push”. However it allows for a few things:
- It allows you to contribute to another repo without needing administrative privileges to make changes to the repo.
- It allows others to review your changes and suggest corrections, additions, edits, etc..
- It allows repo administrators control over what gets added to their project repo.
The ability to suggest changes to ANY repo, without needing administrative
privileges is a powerful feature of GitHub. In our case, you do not have privileges
to make changes to the earthlab/14ers-git repo. However, you can make as many changes
as you want in your fork, and then suggest that Earth Lab incorporate those changes
into their repo, using a pull request.
Pull requests in GitHub
This section was adapted from the GitHub Hello World guide. They provide an animated version of these directions.
Pull requests are the heart of collaboration on GitHub. When you open a pull request, you’re proposing your changes and requesting that someone review and pull in your contribution and merge them into their project.
Pull requests show diffs, (differences), of the content between your repo and the repo that you are submitting changes to. The changes, additions, and subtractions are shown in green and red.
Step 1 - Start Pull Request
To begin a pull request (PR), click the pull request button on the main repo page.
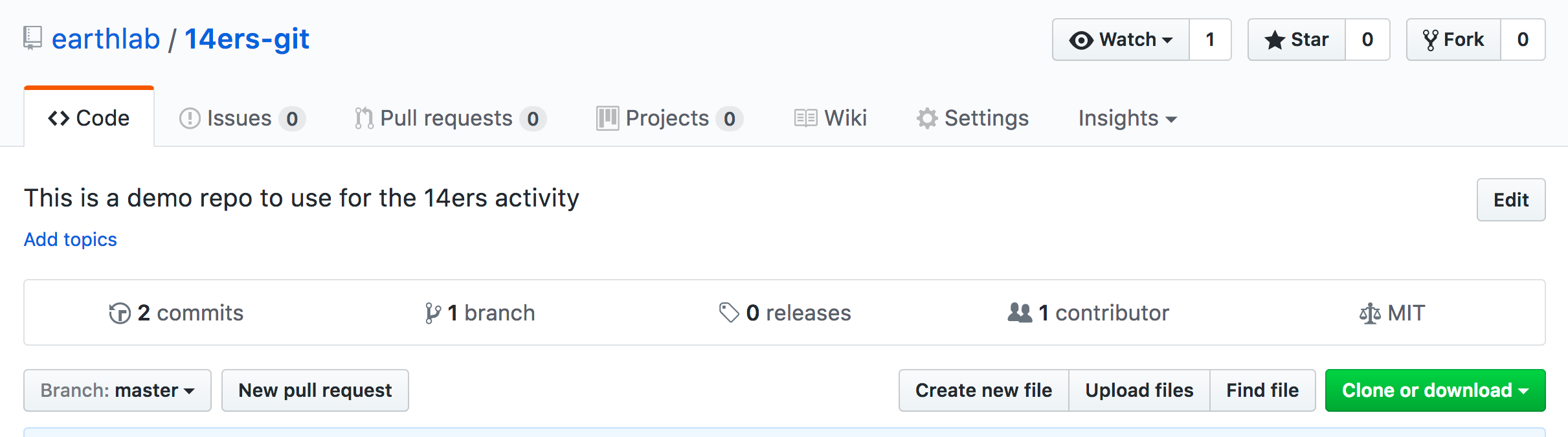
Data Tip: You can also click the “Pull requests” tab at the top of the page to submit a pull request. When the pull request page opens, click the “New pull request” button to initiate the PR.
Step 2 - Which repo to update - select your base & head
Next you need to select which repo you wish to update (the base repo) and which repo contains the content that you wish to use to update the base (the head repo). In this example, you want to update earthLab/14ers-git with commits in your fork YOUR-USERNAME/14ers-git.
Head vs Base
- Base: the repo that will be updated, the changes will be added to this repo.
- Head: the repo from which the changes come.
One way to remember this is that the “head” is ahead of the base. So we must add from the head to the base.
When you begin a pull request, the head and base will auto-populate as follows:
- base fork: earthlab/14ers-git
- head fork: YOUR-USERNAME/14ers-git
The above pull request configuration tells Git to update the Earth Lab repo with contents from your repo.
Step 3 - Verify changes
When you compare two repos in a pull request page, GitHub provides an overview of the differences (diffs) between the files. Look over the changes and make sure nothing looks surprising.
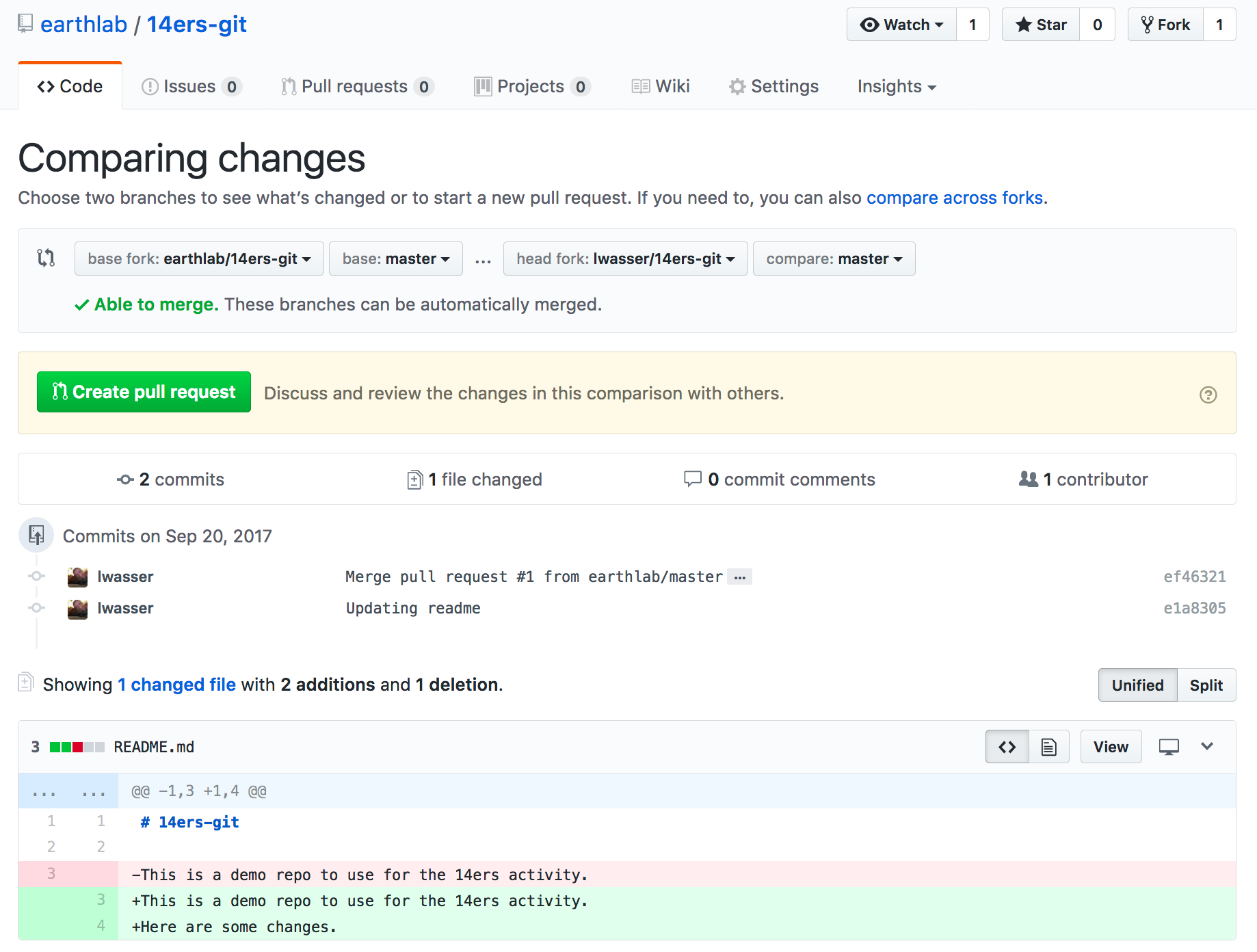
Step 4 - Create a pull request
If you are adding new commits to the Earth Lab repo, then the pull request button will be available. Click the green “Create Pull Request” button to submit your pull request.
Step 5 - Describe your pull request using a short title
Give your pull request a title and write a brief description of your changes. When you’re done with your message, click “Create Pull Request”.
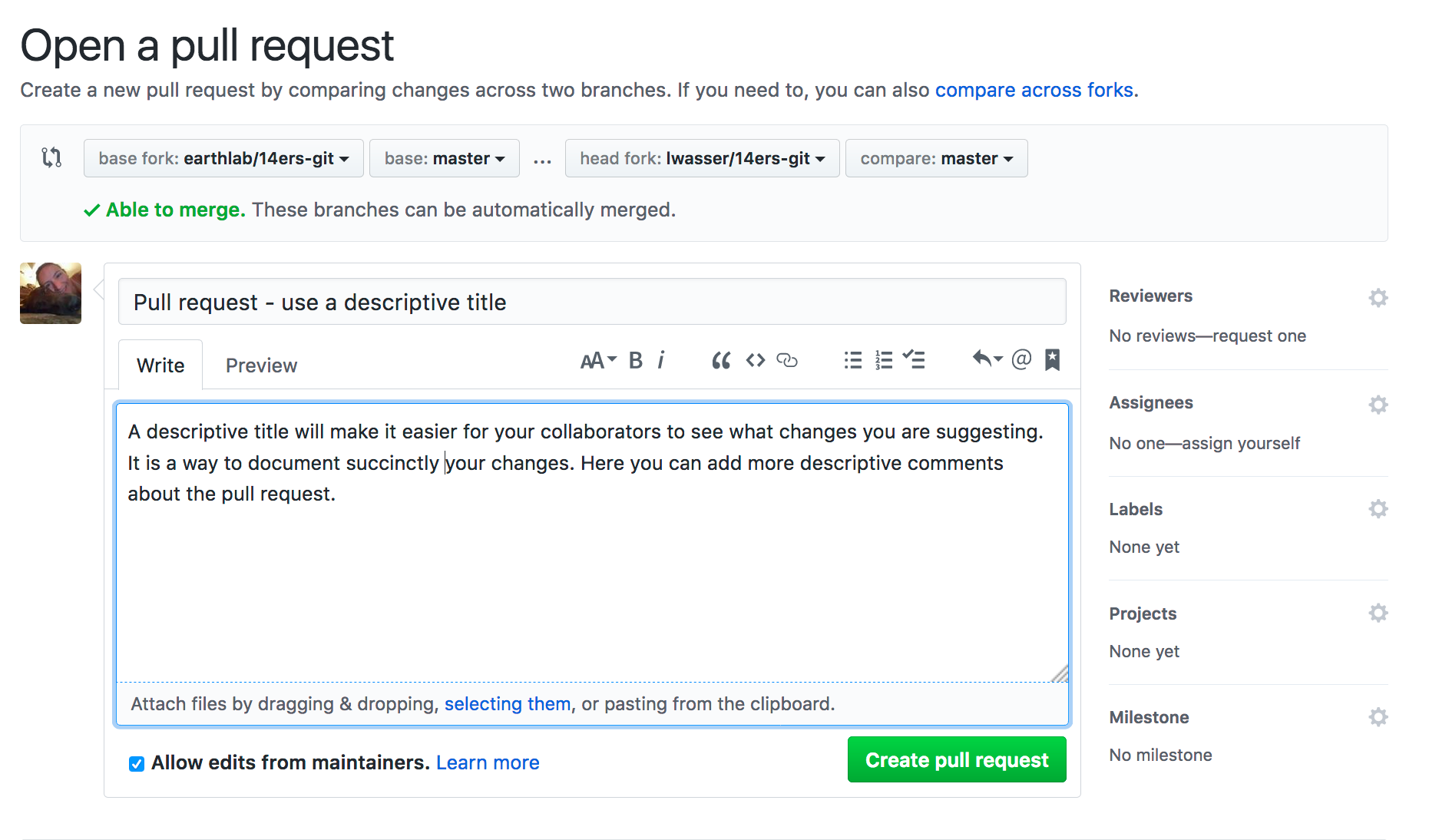
Notice the repo name up at the top (in your repo and in screenshot above) When creating the pull request you will be automatically transferred to the base repo. Since your fork was the base (we are updating it), GitHub will transfer you to your github.com fork landing page.
Challenge - Submit Pull Request to update a 14er markdown file
Within the 14er repo, you will find a list of .md - one for some of the tallest
14ers in Colorado.
On your computer, do the following
- Select a 14er markdown file that you’d like to update.
- Look up the elevation and location (longitude, latitude in decimal degrees) for the 14er
- Add that information and an interesting fact or so about the 14er to the appropriate 14er markdown file.
Next
- Save your file, add and commit your changes and then push the changes to your fork on GitHub.
- Submit a pull request to the
earthLab/14ers-gitrepo.
HINT:
- base fork: earthlab/14ers-git
-
head fork: YOUR-USER-NAME/14ers-git
- Finally, go to the Earth Lab 14ers repo on GitHub. Look for the “Pull Requests” link at the top of the page. How many pull requests are there?
- Do you see your pull request?
Data Tip: While you can submit a pull request to any (public) repo on GitHub, you can only merge a PR if you own the repo or have appropriate permissions. You don’t have contributor permissions to the Earth Lab repo. Thus the workshop instructors will merge the pull requests as they are submitted during the workshop.
Workflow summary
Syncing repos with pull requests
On GitHub:
- Fork the earthlab/14ers-git repo to your GitHub account.
On your computer:
- Clone the repo to your computer locally (you’ll only do this once)
- Edit any files that you wish to change
addandcommityour changes to your repositorygit pushyour changes up to your fork on GitHub
On GitHub:
- Button: Create New Pull Request
- Set base: earthlab/14ers-git, set head: your fork
- Make sure changes are what you want to sync
- Button: Create Pull Request
- Describe the Pull Request using a succinct title & descriptive comments
- Button: Create Pull Request
Remember that you can only merge the pull request if you have contributor permissions to the repo!
Data Tip: Are you a Windows user and are having a hard time copying the URL into shell? You can copy and paste in the shell environment after you have the feature turned on. Right click on your bash shell window (at the top) and select “properties”. Make sure “quick edit” is checked. You should now be able to copy and paste within the bash environment.
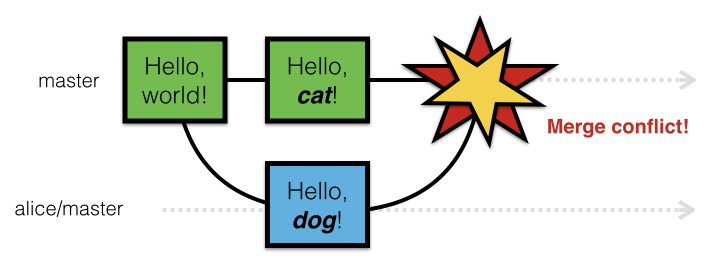
What’s A Merge Conflict?
A merge conflict occurs when two users edit the same part of a file at the same time. Git cannot automatically determine which edit should be in the most current copy. Hence the conflict.
Additional Resources
- Diagram of Git Commands – this diagram includes more commands than we will cover in this series but includes all that we use for our standard workflow.
- GitHub Help Learning Git resources.
Share on
Twitter Facebook Google+ LinkedIn
Leave a Comment